
anatomy of a dog Google Search Dog anatomy, Dog animation, Dog pictures
Dogs also have organs that are vital to their survival, such as the heart, lungs, and liver. The anatomy of a dog can vary depending on their breed. For example, a Greyhound has a lean and muscular body that allows them to run at incredible speeds, while a Bulldog has a stocky and powerful build that makes them great for activities like weight.

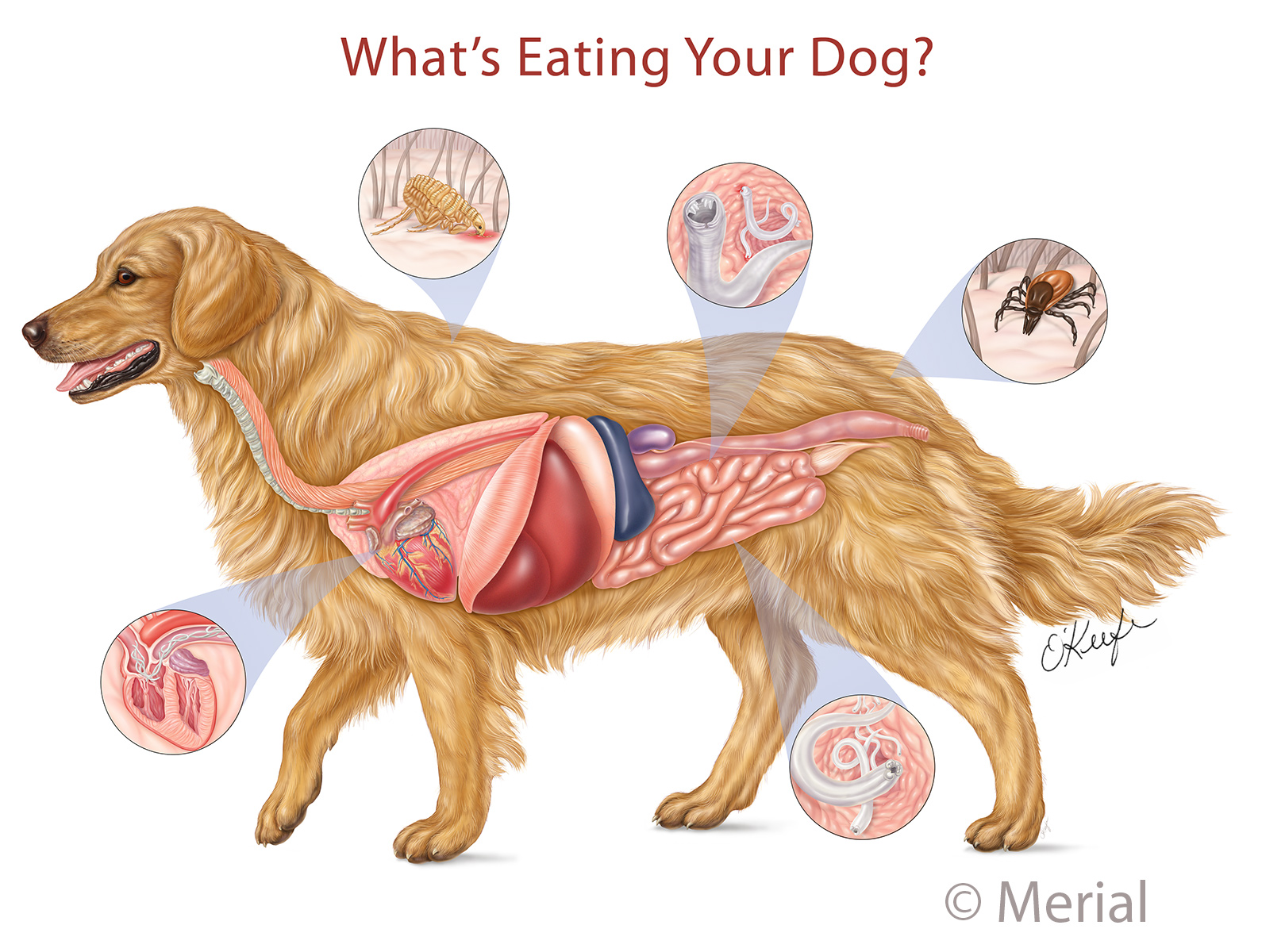
Organe Hund flohbefall erkennen hund
A dog's physical anatomy is designed to help them navigate their environment and perform various tasks. Their bodies are made up of many different parts, including their skeleton, muscles and internal organs. One of the most important parts of a dog's anatomy is their skeleton. A dog's skeleton is made up of many different bones, which provide.

dog external anatomy
Dog Anatomy Dogs grow in various sizes and shapes. The Greyhound is the 'Fastest Dog on Earth' and can run 45 miles per hour for short periods of time. The Irish Wolfhound is the largest dog standing 28 - 32 inches and weighing between 90 - 150 pounds.

dog anatomy Dog Care Training Grooming
The Anatomage Dog is the first highly detailed dog anatomy atlas that comprehensively features internal organs, including vascular systems and muscular-skeletal structures. Originating from real dog data, the Anatomage Dog exhibits the highest level of anatomical accuracy. All of its volumetric 3D and individual structures are segmented, users.

Anatomy of a male dog crosssection, showing the skeleton and internal
Dog - Muscles Dog - Thorax/Abdomen/Pelvis Animal - Anatomy atlas: Cardiovascular system Veterinary anatomy - Animal: ANATOMICAL PARTS Abdomen Abdominal aorta Abdominal mammary gland Abdominal mammary region Accessory carpal bone Acromion Adductor muscle Ala of ilium; Wing of ilium Ala of nose Anconeus muscle Antebrachial region Aortic arch
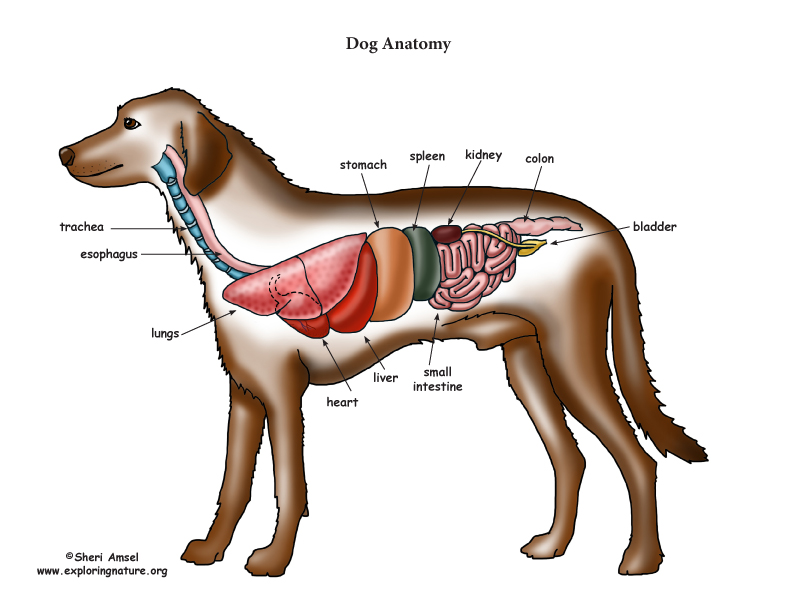
Dog Anatomy (Thoracic and Abdominal Organs)
This vet-Anatomy module presents an anatomy atlas of the abdomen and pelvis of the dog in CT. CT images are from a healthy 6-year-old castrated male dog. This module displays cross-sectional labeled anatomy images of the canine abdominal cavity and the pelvis on a Computed Tomography (CT) and 3D images of the abdomen of the dog.
female dog body parts diagram
Anatomic Planes. The main planes of motion for dogs are as follows (see Figure 5-1): • The sagittal plane divides the dog into right and left portions. If this plane were in the midline of the body, this is the median plane or median sagittal plane. • The dorsal plane divides the dog into ventral and dorsal portions.

Внутренние органы собаки. Вид справа Dog Internal Organs, Anatomy
Thighs: The upper thigh is above the knee of the hind leg. The lower thigh is beneath the knee. Stifle: The stifle, or knee, sits on the front of the hind leg. It falls in alignment with the abdomen. Hock: The hock is also known as the harsus. This is the joint on the dog's hind legs that makes an awkward sharp angle.
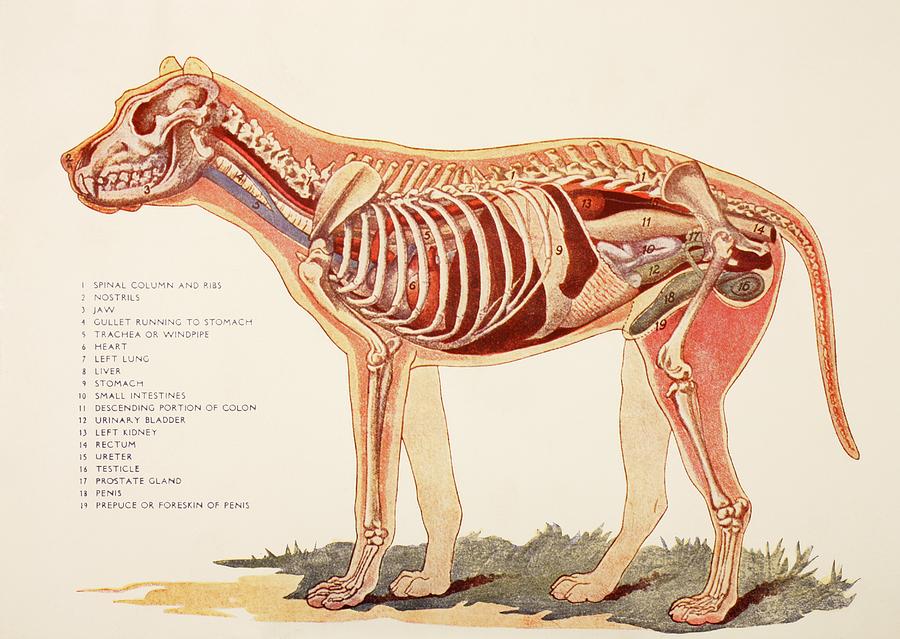
Internal Organs Of A Male Dog. From Photograph by Ken Welsh Fine Art
This module of vet-Anatomy is a basic atlas of normal imaging anatomy of the dog on radiographs. 51 sampled x-ray images of healthy dogs performed by Susanne AEB Borofka (PhD - dipl. ECVDI, Utrecht, Netherland) were categorized topographically into seven chapters (head, vertebral column, thoracic limb, pelvic limb, larynx/pharynx, thorax and abdomen/pelvis).
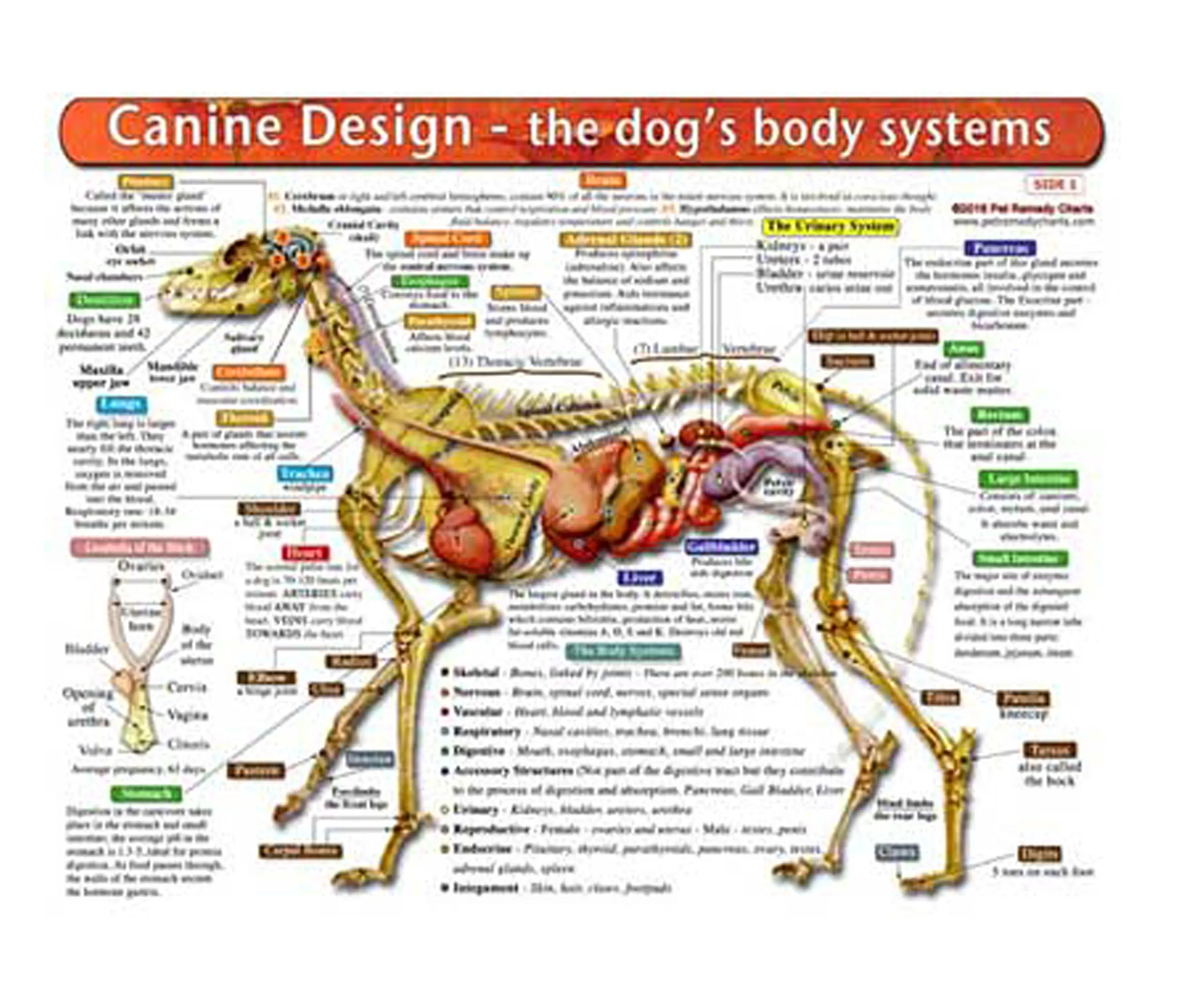
Buy The Dogs Body Systems A DoubleSided, UV Protected, Laminated Dog
Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds. Would you be surprised to know that short dogs are more aggressive? Or taller dogs are more affectionate?
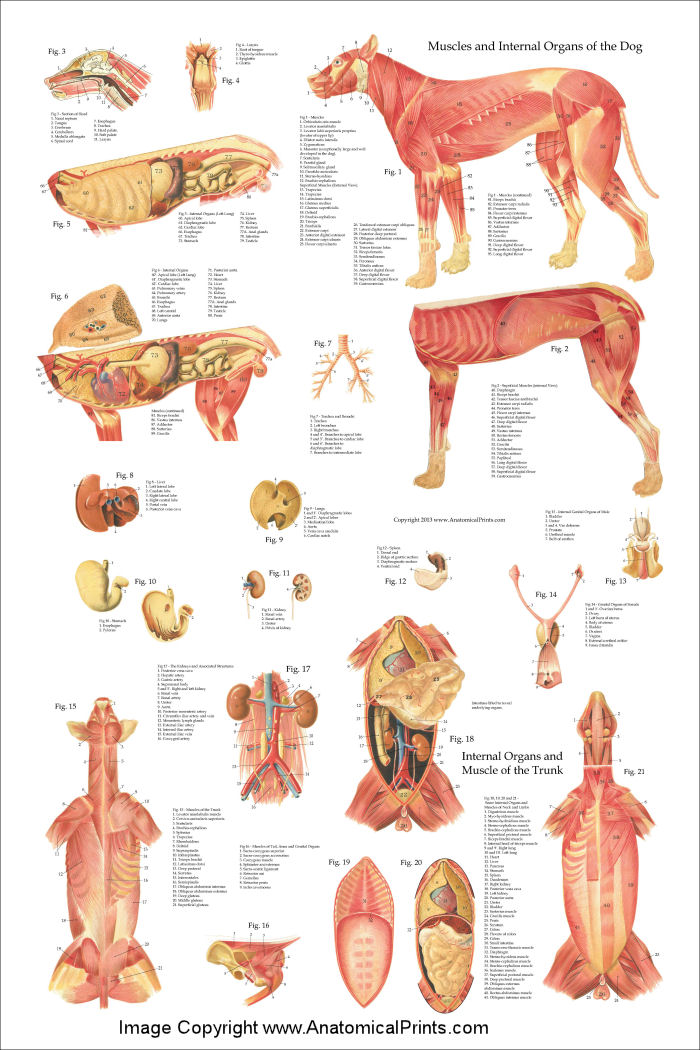
Dog Internal Anatomy Poster 24 x 36
Common anatomical terminology Here are some common veterinary terms and their meanings: Pet senses Pets communicate in a very different way than people do. They have the same basic senses like sight, hearing, smell, touch, and taste, but they use them differently to communicate with the world.
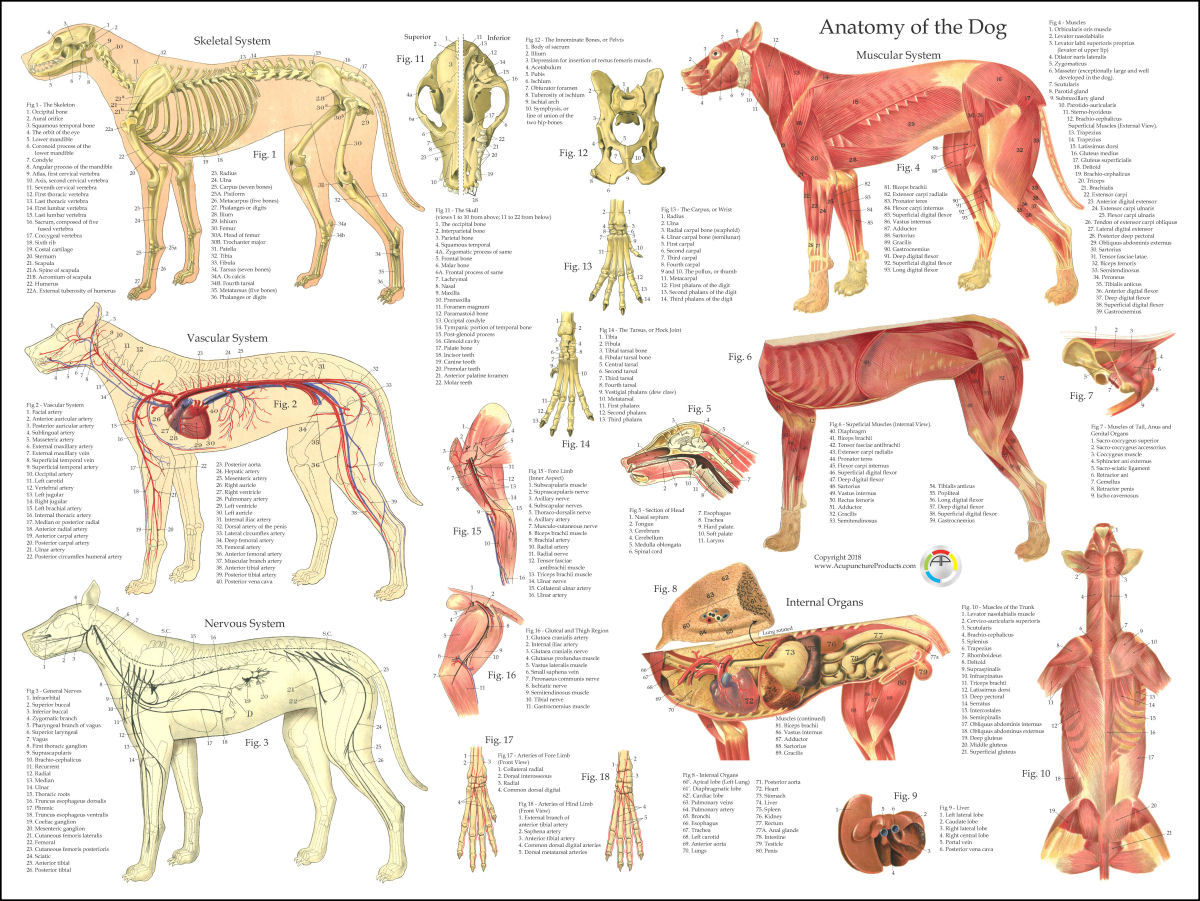
Dog Muscle Skeletal Veterinary Internal Anatomy Poster 18 X 24
Have comments? Anatomy Study Resources This guide contains a variety of resources to help with the study of veterinary anatomy. Included are web resources, books (both print and electronic), and specialty resources such as flashcards. For suggestions or comments, please submit them via the Have comments tab. Anatomy No-Cost Web Resources

Dog Internal Anatomy Poster Dog anatomy, Anatomy, Vet medicine
On the left side view of a dog's internal organs, you can see the lungs, heart, liver, stomach, spleen, kidney, intestines, bladder, and the rectum in that order from front to back. You can also view the spinal column and the brain. Laurie O'Keefe Dog Anatomy Organs Right Side

Dog Internal Organs Anatomy Anatomy Of A Male Dog stock photo iStock
Dog anatomy comprises the anatomical studies of the visible parts of the body of a domestic dog.Details of structures vary tremendously from breed to breed, more than in any other animal species, wild or domesticated, as dogs are highly variable in height and weight. The smallest known adult dog was a Yorkshire Terrier that stood only 6.3 cm (2.5 in) at the shoulder, 9.5 cm (3.7 in) in length.
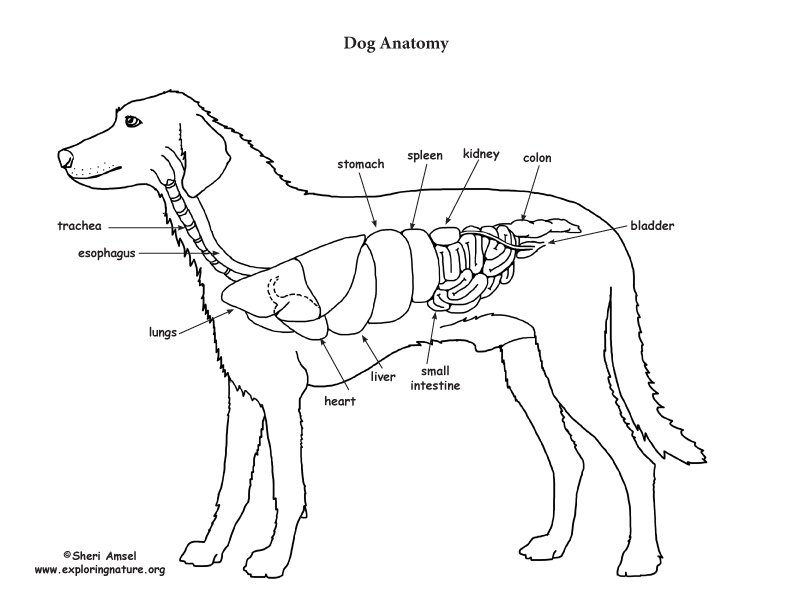
Dog Anatomy (Thoracic and Abdominal Organs)
Trachea Lungs and Smaller Airways (bronchi and bronchioles) Dog Mouth Lungs Cat Chest Dog Chest Special Senses The organs of special senses allow the animal to interact with its environment; sight, taste, smell and hearing. Cat Eyes Dog Eyes Dog Ears Urogenital System
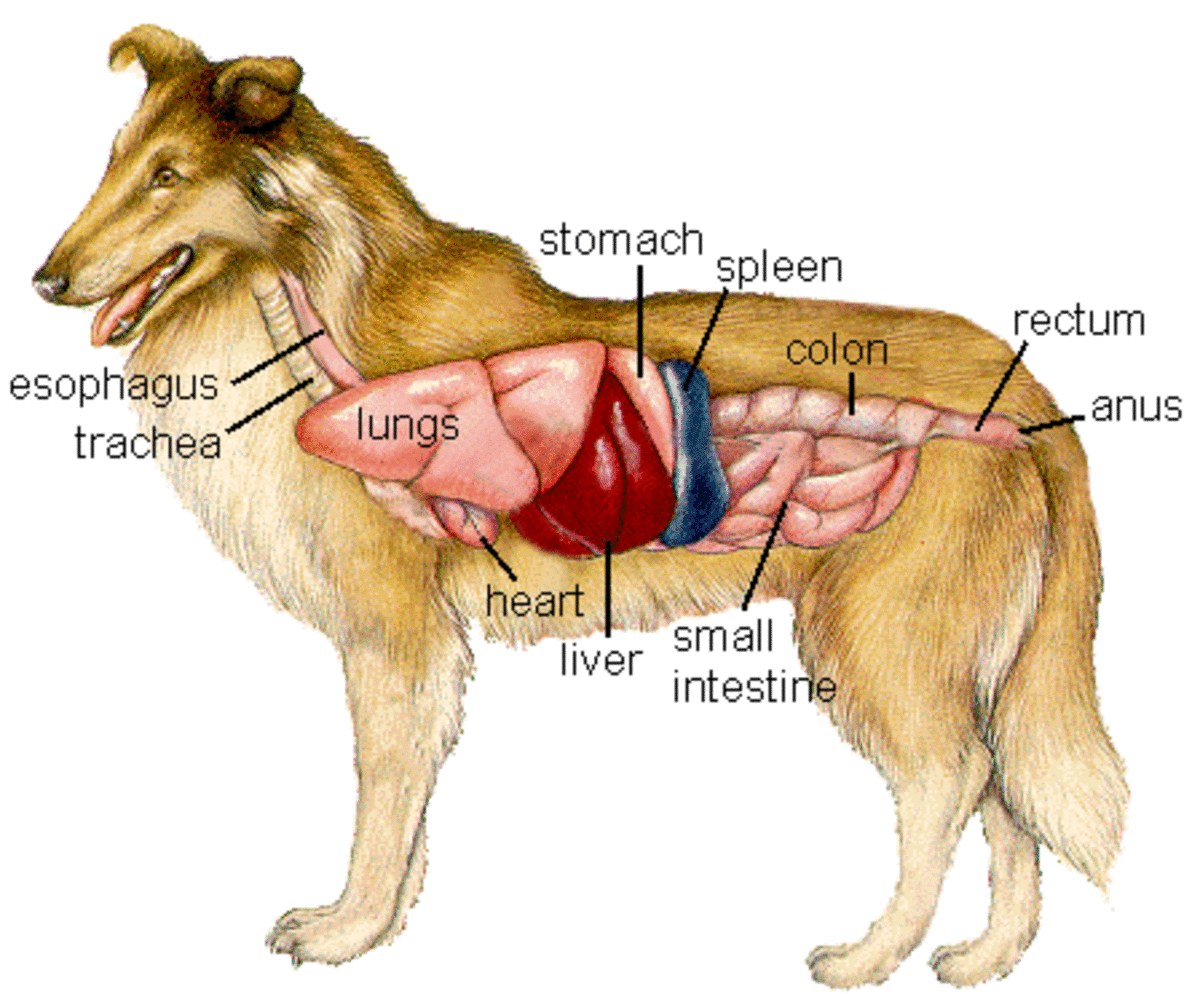
Coughing in Dogs May Signal Heart Disease HubPages
The anatomy of a dog includes its skeletal structure, reproductive system, the internal organs, and its external appearance. The following paragraphs explain all these aspects in brief, along with diagrams, which will help you understand them better. External Anatomy Dogs, like all mammals, have eyes, a nose, a forehead, and ears.