
Relative clauses Grammar KS4 German teaching resource Teachit
Relativsätze im Deutschen - Erklärungen und Beispiele German Relative Clauses - Summary Zusammenfassung Relative clauses are subordinate clauses which are used as an attribute for a noun. They are always come with relative pronouns. Relative pronouns are, for example, ""der, die, das, welcher, welche, welches".
Relative Clauses German / (Relative Pronouns and Relative Clauses in German) PPT Powerpoint
In German, word order in complex sentences with multiple relative clauses can be flexible. While the technical rules suggest placing the verb at the end of each clause, in practice, verbs are often rearranged for clarity and fluidity. Practice Makes Perfect. Mastering relative pronouns and clauses in German takes practice.

German Grammar Relative Pronouns and Relative Clauses YouTube
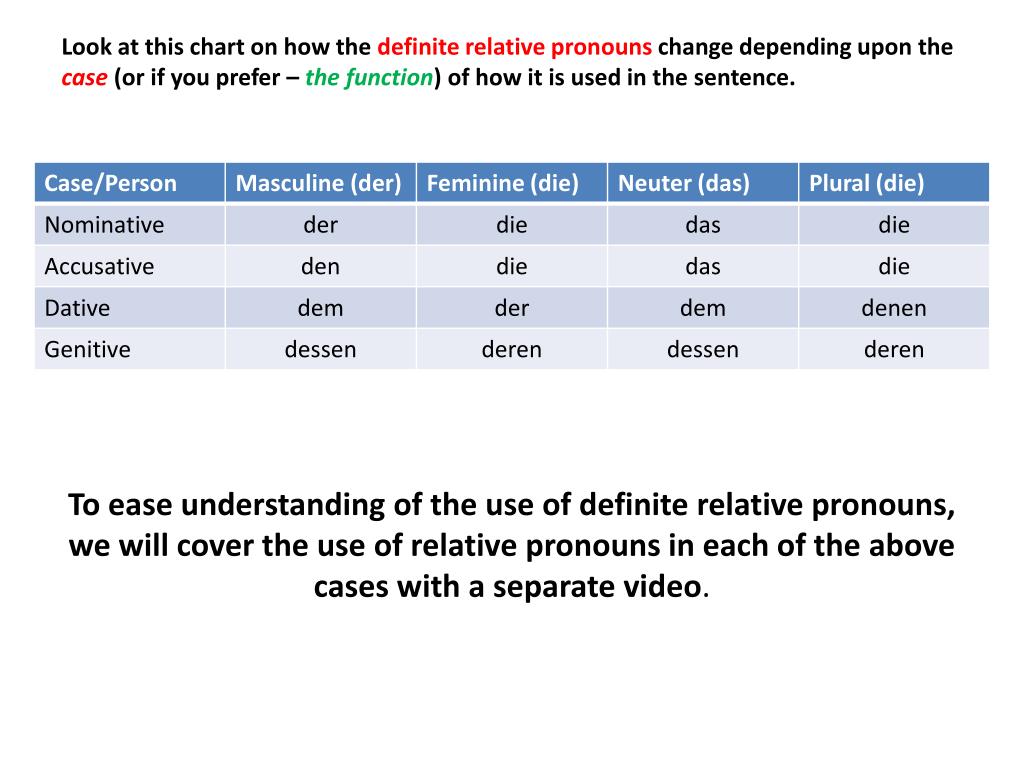
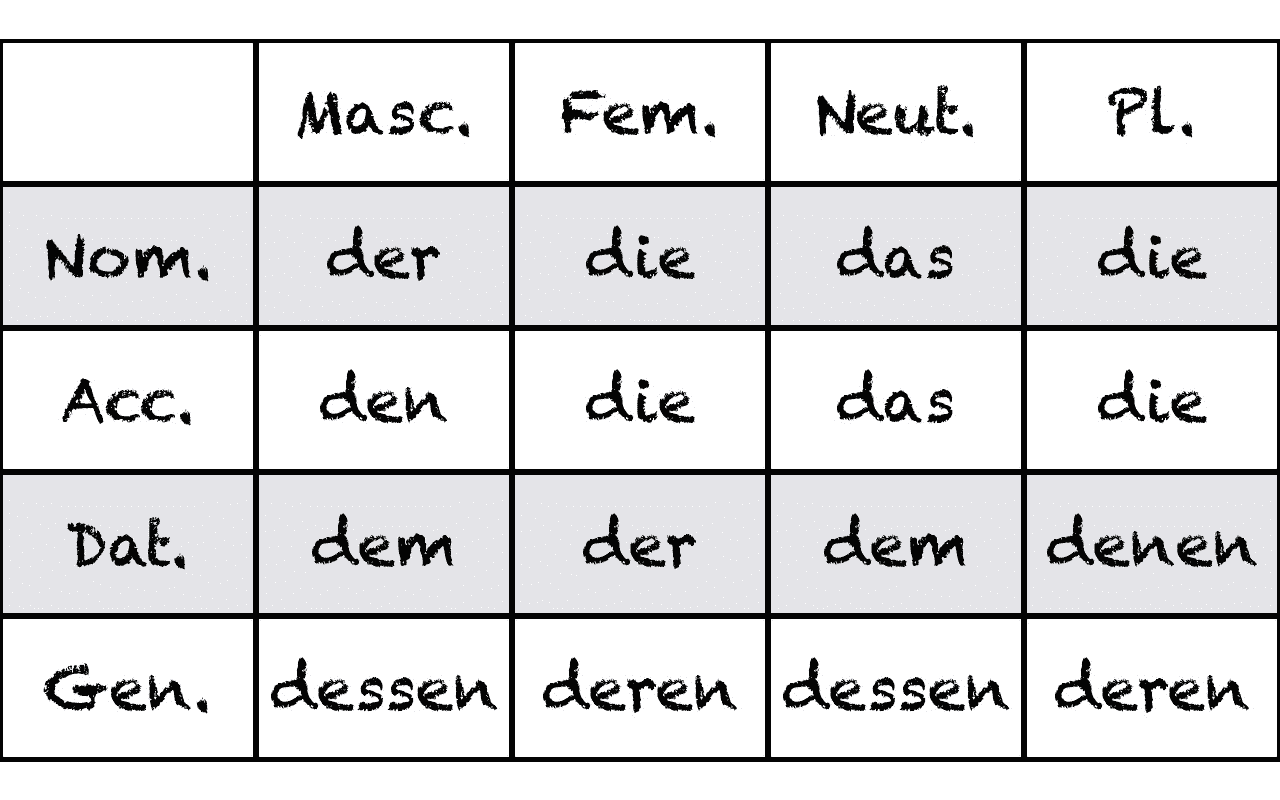
What the German relative pronouns are (with a chart!) How to know which relative pronoun to use How sentence structure is impacted by relative pronouns The Basics of Relative Pronouns Pronouns in general replace other nouns / noun phrases so that we don't have tediously (or at least obnoxiously) repeat ourselves.

Relativsatz im Akkusativ in 2020 Learn german, German grammar, German language learning
Relative Clauses German: Relative Clauses This guide offers resources on German language, literature, culture, history, and current affairs. Relative Clauses Doc Pusto's printable version. Getting the right relative pronoun: A "common element" refers to the same person or thing, and therefore has identical gender and number.
Relative Clauses German / (Relative Pronouns and Relative Clauses in German) PPT Powerpoint
Grammar Relative clauses Summary: relative clauses Relative clauses are subordinate clauses. As a rule, they cannot stand alone and are dependent on a superordinate main clause or.

German Relative Pronouns Learn German with Herr Antrim
German only rarely omits the relative pronoun as we often do in English: "The book he is reading is interesting." Thus, normally, the relative pronoun will be the first word in the clause, unless it is used with a preposition, which will precede it - see example #6 below. German marks both the beginning and the end of the relative clause.

More work with relative pronouns in German YouTube
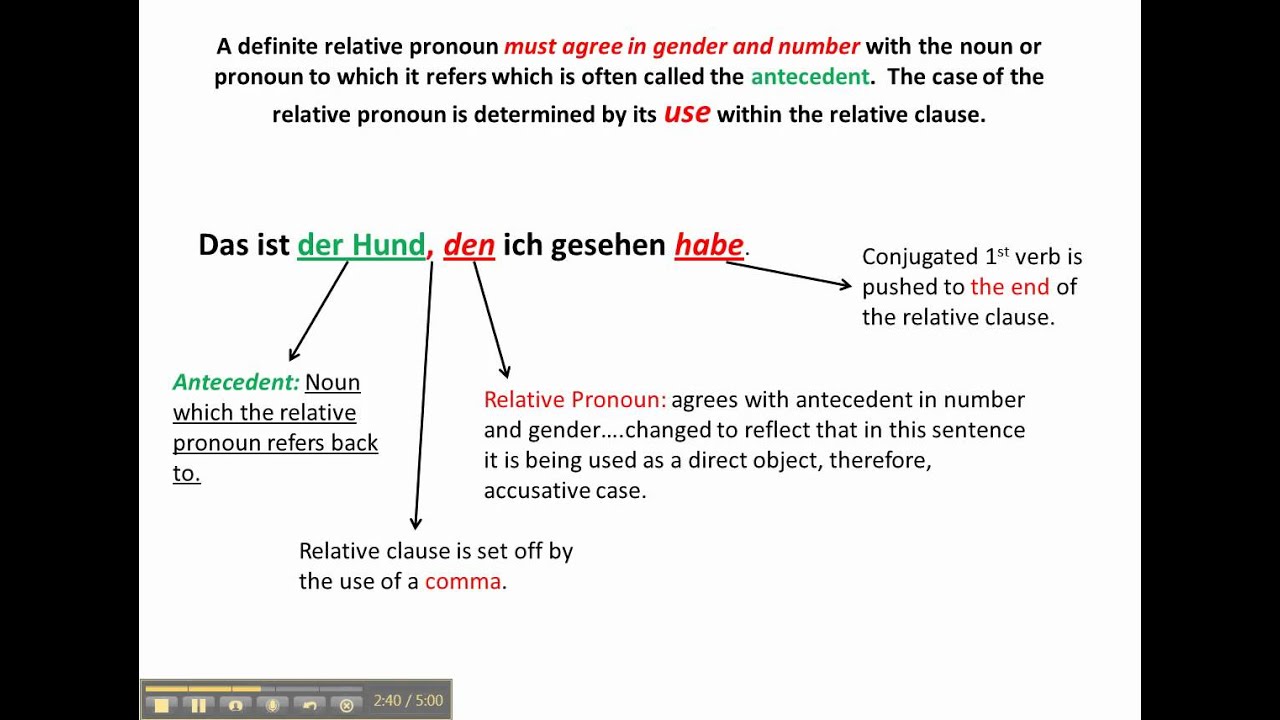
In the forms der, die and das, the relative pronouns introduce relative clauses in the nominative. The antecedent in the main clause defines the grammatical gender and number (singular or plural) of the pronoun. The case is defined by the role of the relative pronoun in the subordinate clause. If the relative pronoun in the subordinate clause.
Relative Clauses German / (Relative Pronouns and Relative Clauses in German) PPT Powerpoint
Relative Clauses in German: German relative clauses perform the same function as in English, but there are differences in form: The relative pronouns reflect gender, number, and case. The relative pronoun's antecedent determines gender and number, while the pronoun's function within the dependent clause determines the case (see the examples below).

Struggling with Relative Clauses in German? Then read this Relative clauses, German grammar
In German, the relative pronoun for people and things will be a form of der/das/die ==> in particular, do not use wer (or wen or wem) to translate English who or whom: Da ist der Mann, der Rumpelstilzchen liebt. Da ist der Mann, wer Rumpelstilzchen liebt. There is the man who loves Rumpelstilzchen.

German Relative Clauses Learn German with
German Relative Clauses - The Basics | Your Daily German < Previous Lesson Next Lesson > Relative Pronouns in German In this episode: A fun look at the basics of relative clauses in German, how they're completely different than in English and the one thing that unites all relative clauses world-wide. 83 Comments Hello everyone,
Relative Pronouns in German Introduction YouTube
5. Word Order in German Relative Clauses. The word order in German relative clauses follows the rule of placing the conjugated verb at the end of the clause. For example: Die Frau, die am Wochenende einen Kuchen gebacken hat, ist meine Tante. "The woman, who baked a cake on the weekend, is my aunt."

German Relative Clauses Easily Explained
The German relative pronouns in the different cases are exactly the same as the definite article, except for those bolded below.. There are two rules in German that make recognizing relative clauses easier than in English: German only rarely omits the relative pronoun as we often do in English: "The book he is reading is interesting." Thus.

learn German Relative Sentences English subs YouTube
Hence they refer back to a word in the main clause. Usually the relative clause comes directly after the word it modifies and is separated by a comma. If the independent clause continues after the relative clause, then a comma comes after the relative clause as well. Examples: Der Mann hat ein blaues Auge. Fußballfans haben den Mann geschlagen.

Relative pronouns in German practice activities YouTube
The relative clause always comes right after the noun it is describing. Here are some more examples. In. Note in the first two pairs of examples that the possibility of using was to refer to the entire previous clause enables German to make some distinctions that English has to leave ambiguous: Viele Leute kaufen die neueste Justin.

German relative pronouns and relative clauses made clear
2 Types of Relative Clauses 2.1 Nominative 2.2 Accusative 2.3 Dative 2.4 Genitive Du bist der Mann, den ich liebe You are the man that I love You should have the following in mind about relative clauses in German: - the conjugated verb is placed at the end of the relative clause. - sometimes a comma is placed in front of the relative pronoun.
Relative Pronouns and Relative Clauses German on the Web
Choose the correct relative pronoun. Das sind die Kinder, wir eine Geschichte vorgelesen haben. Dort steht der neue Lehrer, Geschichte unterrichtet. Wo ist der Joghurt, ich mir gekauft habe? Wer ist die Frau, Gepäck vor dem Hotel steht? Das ist das Restaurant, in wir gerne essen. Turn the underlined sentence into a relative clause.