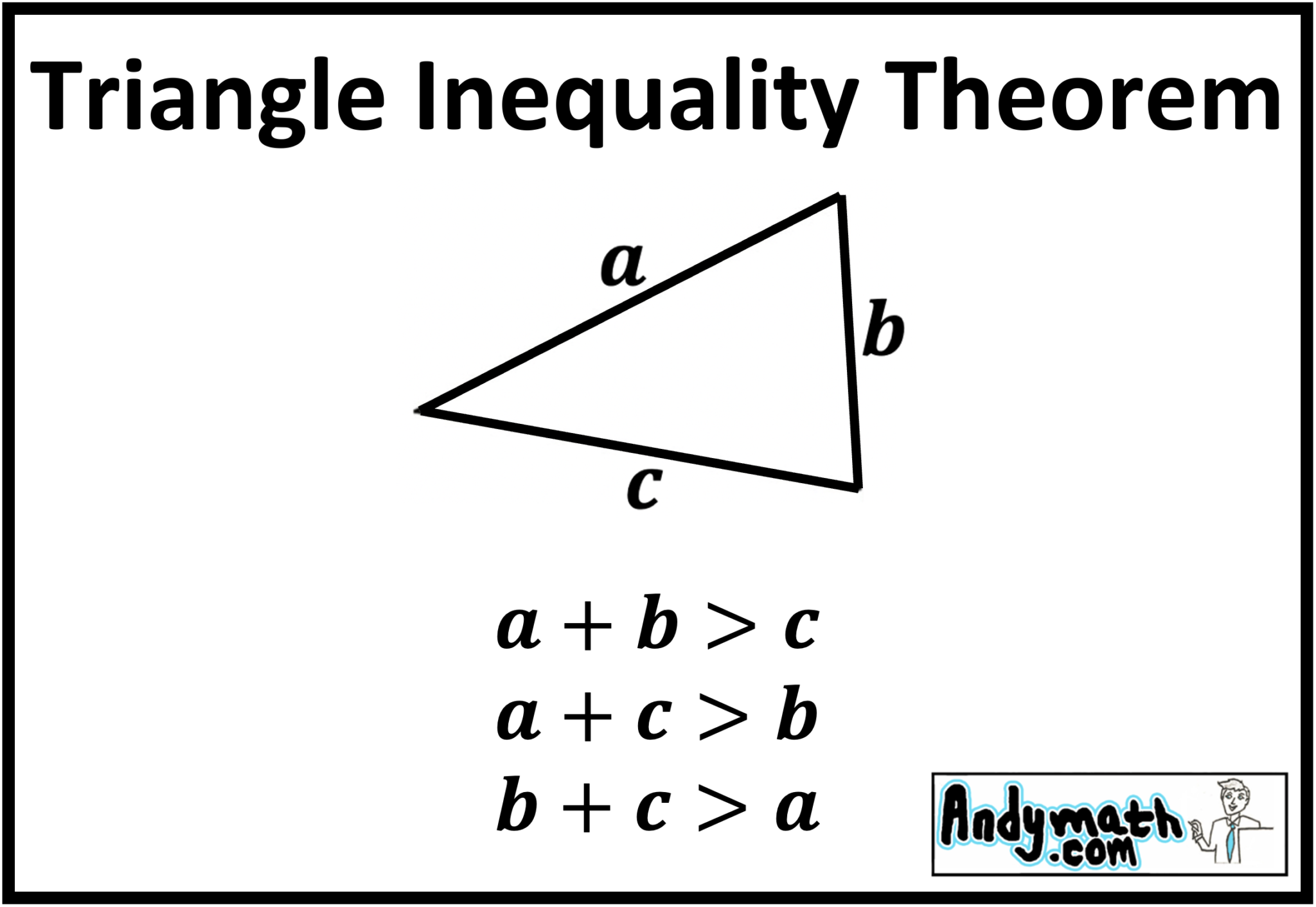
Triangle Inequality Theorem
Triangles. In Geometry, a triangle is a three-sided polygon that consists of three edges and three vertices. The most important property of a triangle is that the sum of the internal angles of a triangle is equal to 180 degrees. This property is called angle sum property of triangle.

Triangle Congruence Theorems SAS, ASA & SSS Postulates (Video)
Triangle theorems are based on various properties of this geometrical shape, here are some prominent theorems associated with this is that students must know -. 1. Pythagoras Theorem. Probably the most popular and widely discussed triangle theorems are Pythagoras' one. Pythagoras theorem Class 10 states that 'in a right-angled triangle.
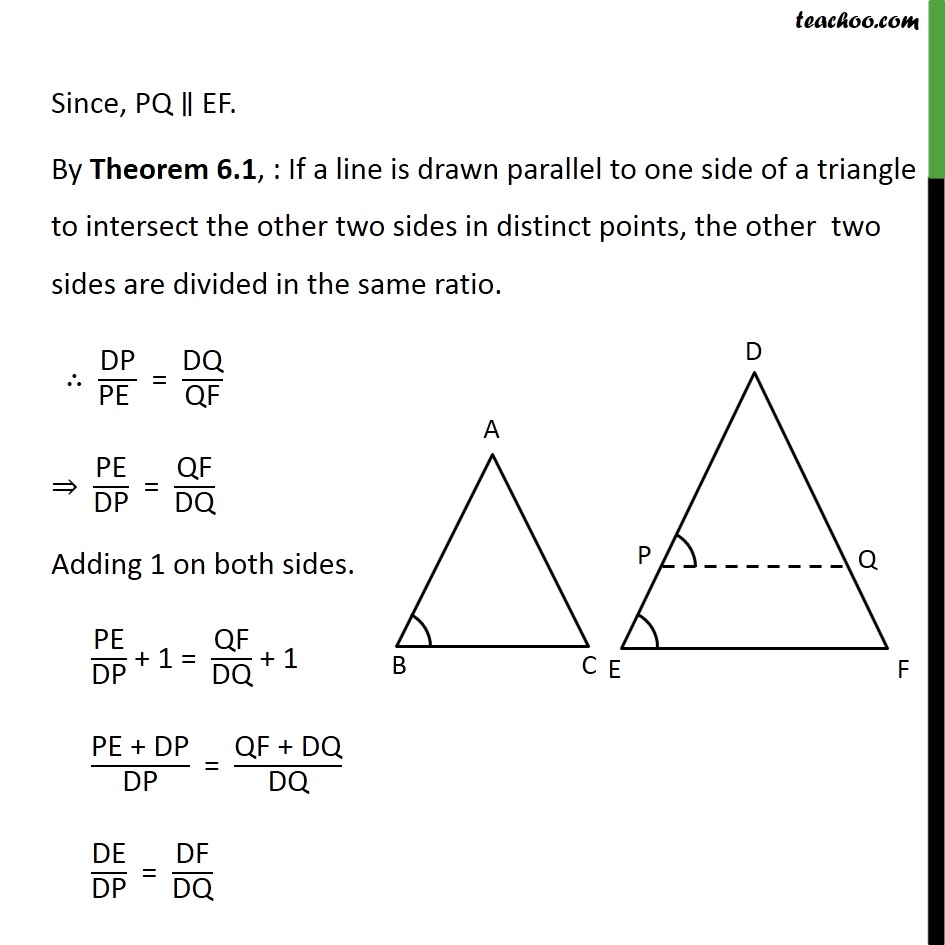
Theorem 6.3 (AAA Similarity) Class 10 If corresponding angles equal
The statement "the base angles of an isosceles triangle are congruent" is a theorem.Now that it has been proven, you can use it in future proofs without proving it again. 3. Prove that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the remote interior angles.
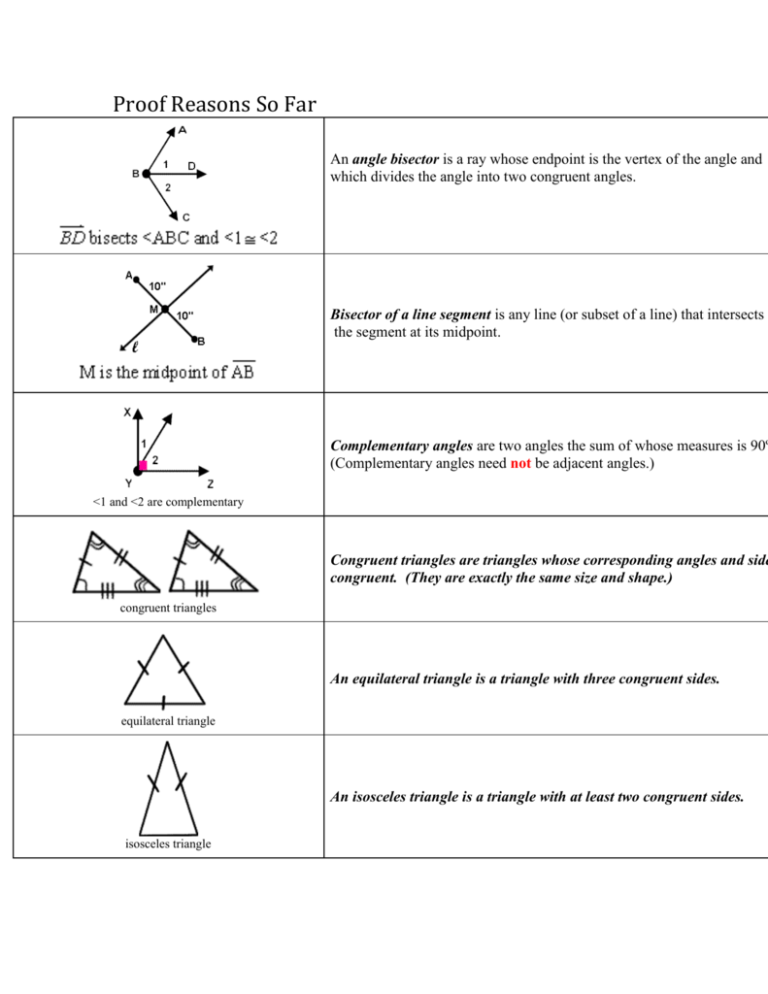
List of Theorems and Keywords so far (Print out)
Geometry, You Can Do It! 2 Triangle Classification by angles An acute ∆ is a ∆ with three acute ∠s. An obtuse ∆ is a ∆ with an obtuse ∠s. A right ∆ is a ∆ with a right ∠. An equilateral ∆ is a ∆ with all ∠s ≅. Angle Theorems: Triangles If I asked an entire class to draw a triangle on a piece of paper, then had each person cut out their

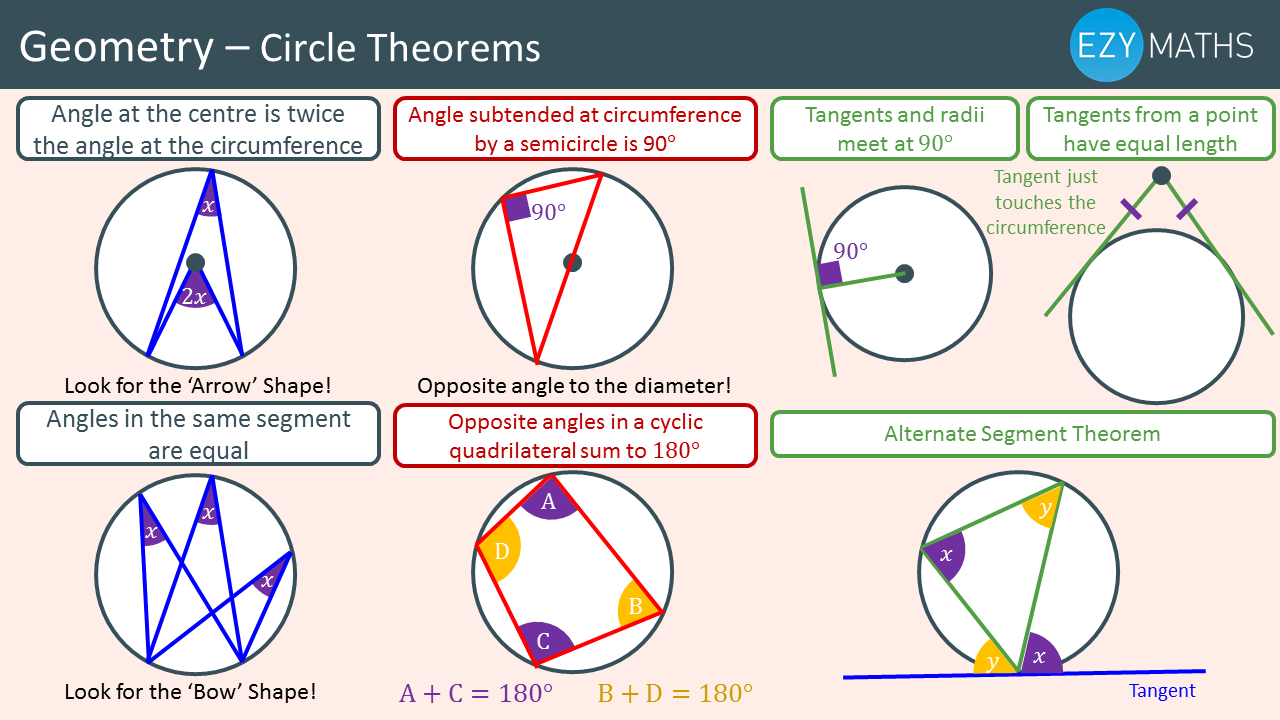
circle theorems geometry Google Search Circle theorems, Math
Math Geometry (all content) Unit 4: Triangles About this unit You probably like triangles. You think they are useful. They show up a lot. What you'll see in this topic is that they are far more magical and mystical than you ever imagined! Triangle types Learn Classifying triangles Classifying triangles by angles
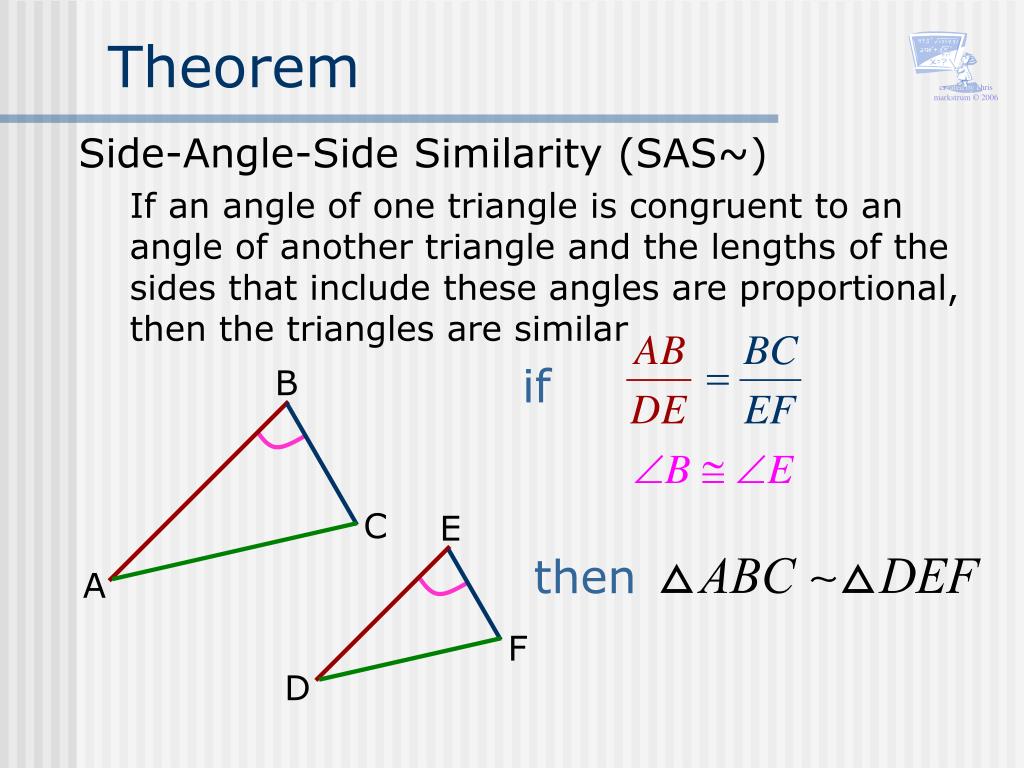
PPT Lesson 8.4 & 8.5 Similar Triangles PowerPoint Presentation ID
Theorem 1: The sum of all the three interior angles of a triangle is 180 degrees. Suppose ABC is a triangle, then as per this theorem; ∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180° Theorem 2: The base angles of an isosceles triangle are congruent. Or The angles opposite to equal sides of an isosceles triangle are also equal in measure.

geometry Triangle question Mathematics Stack Exchange
Use the Pythagorean Theorem. The Pythagorean Theorem is a special property of right triangles that has been used since ancient times. It is named after the Greek philosopher and mathematician Pythagoras who lived around 500 500 BCE.. Remember that a right triangle has a 90° Figure 9.12.. Figure 9.12 In a right triangle, the side opposite the 90° 90° angle is called the hypotenuse and each.
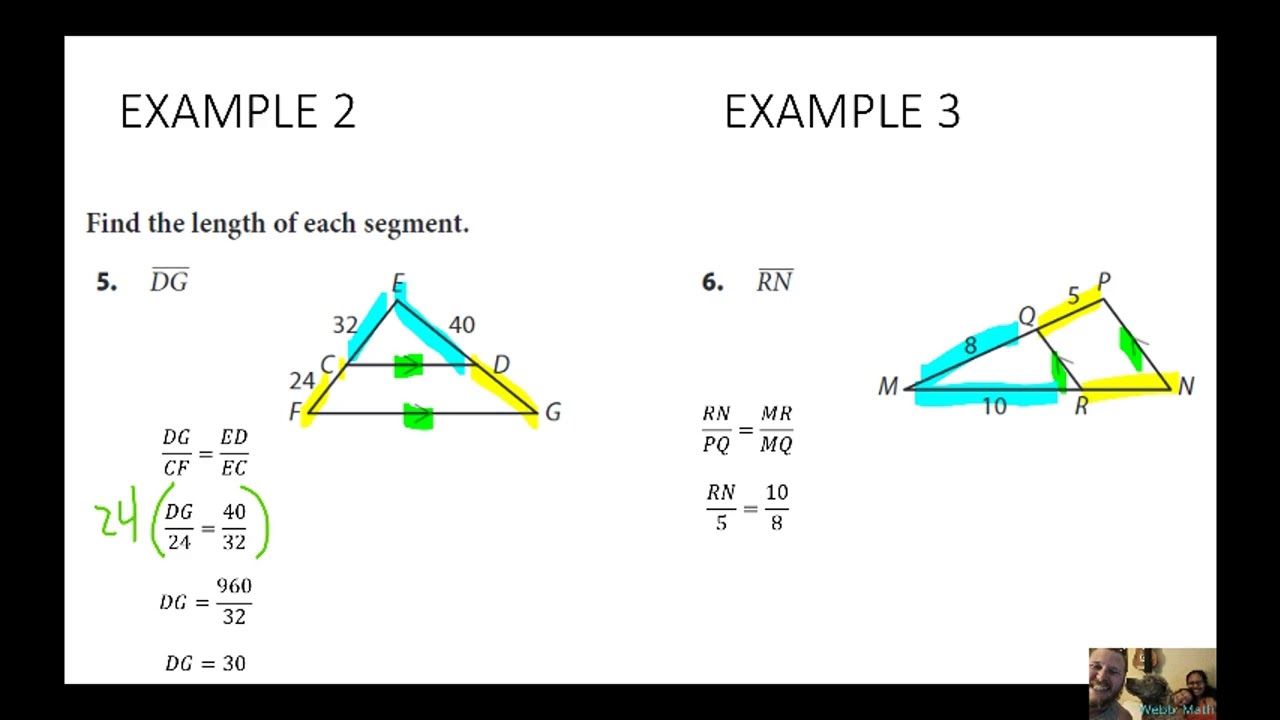
Geometry 12.1 Triangle Proportionality Theorem YouTube
An interior angle is formed by the sides of a polygon and is inside the figure. The 3 interior angles in every triangle add up to 180 ∘ . Example: 48 ∘ 109 ∘ 23 ∘ 109 ∘ + 23 ∘ + 48 ∘ = 180 ∘ Want to learn more about the interior angles in triangles proof? Check out this video. Finding a missing angle
Congruence Theorems Applet
Geometry 2: Congruent Triangles 2.3: The ASA and AAS Theorems Expand/collapse global location

Ratio of areas of two similar triangles activity
Triangles Triangle A triangle is a closed figure in a plane consisting of three segments called sides. Any two sides intersect in exactly one point called a vertex. A triangle is named using the capital letters assigned to its vertices in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. For example, the triangle below can be named triangle ABC in a

Geometry Formulas Triangles Blog Math 123
1) The exterior angle at a given vertex is equal in measure to the sum of the two remote interior angles. These remote interior angles are those at the other two vertices of the triangle. 2) Knowing this, it follows that the measure of any exterior angle is always greater than the measure of either remote interior angle.
List of triangle theorems
The Exterior angle theorem of a triangle states that the exterior angle of a triangle is always equal to the sum of the interior opposite angles. Triangle Formulas In geometry, for every two-dimensional shape ( 2D shape ), there are always two basic measurements that we need to find out, i.e., the area and perimeter of that shape.
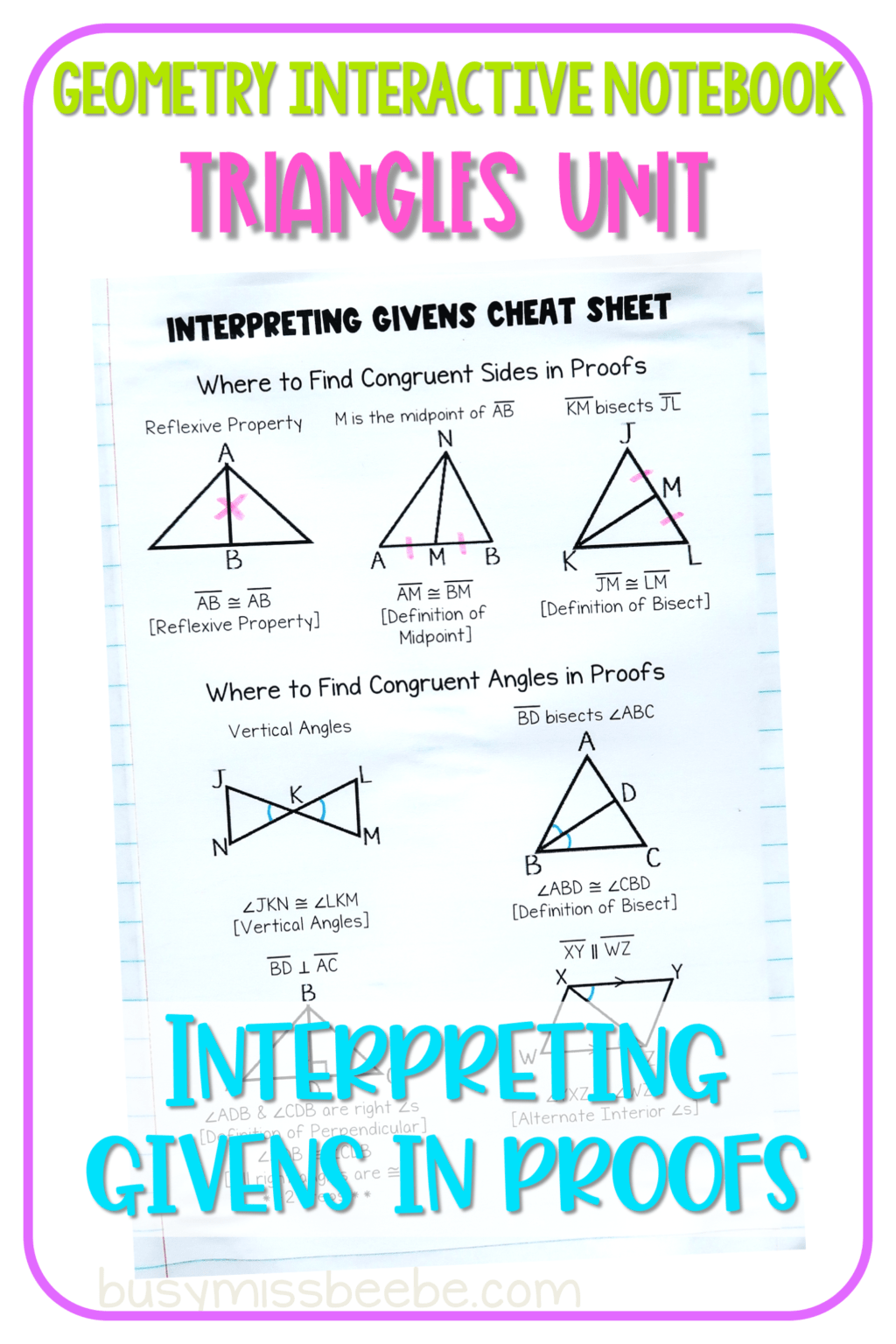
Triangles Geometry Interactive Notebook Busy Miss Beebe
The Pythagorean theorem describes a special relationship between the sides of a right triangle. Even the ancients knew of this relationship. In this topic, we'll figure out how to use the Pythagorean theorem and prove why it works.

Euclid geometry ( Isosceles triangles ; Theorems ; Solving problems
As per the triangle inequality theorem, the sum of the length of the two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side. Observe the figure given above which shows ABC which represents the Triangle inequality property. If a = 4 units, b = 6 units, c = 3 units, let us verify the triangle inequality property as follows: a + b > c ( 4 + 6 > 3)

Circle Theorems Notes Corbettmaths
Geometry Theorems Key components in Geometry theorems are Point, Line, Ray, and Line Segment. Let us go through all of them to fully understand the geometry theorems list. Point In maths, the smallest figure which can be drawn having no area is called a point. Line A straight figure that can be extended infinitely in both the directions Ray

Circle theorems 2 SSDD Problems
Triangles are one of the most fundamental geometric shapes and have a variety of often studied properties including: Rule 1: Interior Angles sum up to 1800 180 0. Rule 2: Sides of Triangle -- Triangle Inequality Theorem : This theorem states that the sum of the lengths of any 2 sides of a triangle must be greater than the third side. )