Partial Mesh Topology YouTube
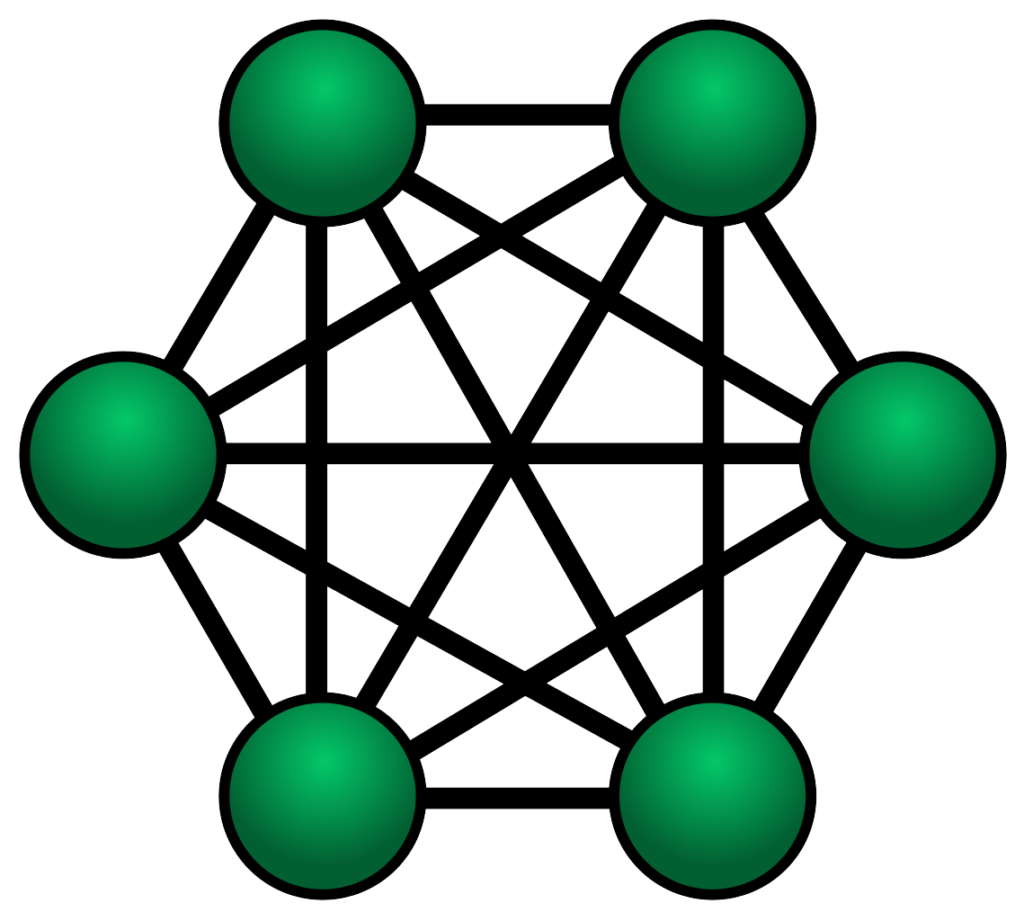
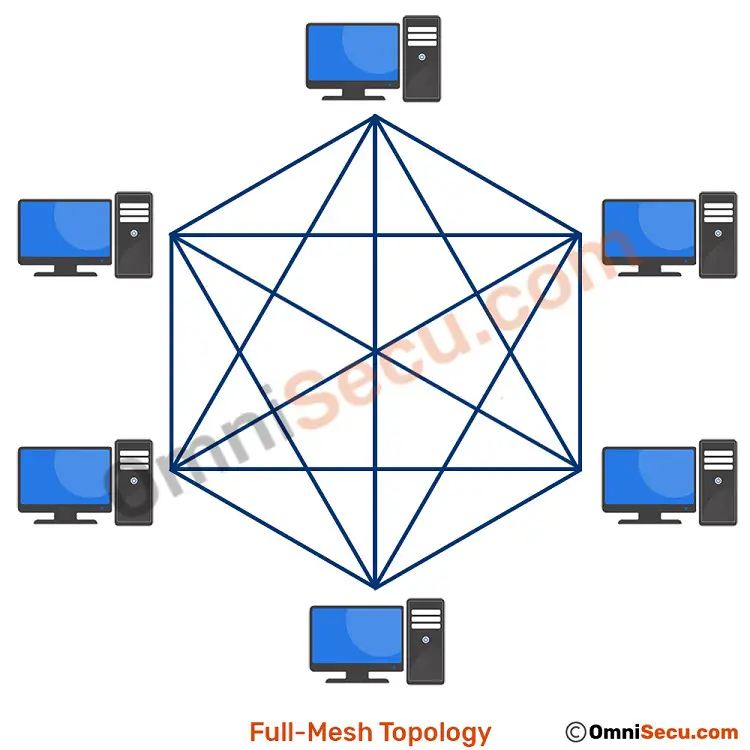
Mesh Topology. The formula w = n (n - 1) / 2, where w is the number of WAN (wide area network) links and n is the number of sites, can be used to determine the number of necessary WAN connections. For instance, 45 WAN connections would be needed to create a fully meshed network for a network with 10 sites: `10 (10 - 1) / 2 = 45`.
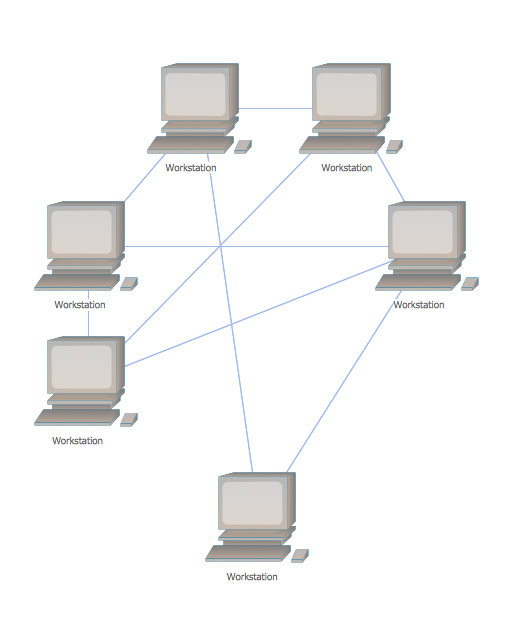
Mesh Topology Diagram Png Instead, each node is connected to at least one other node and
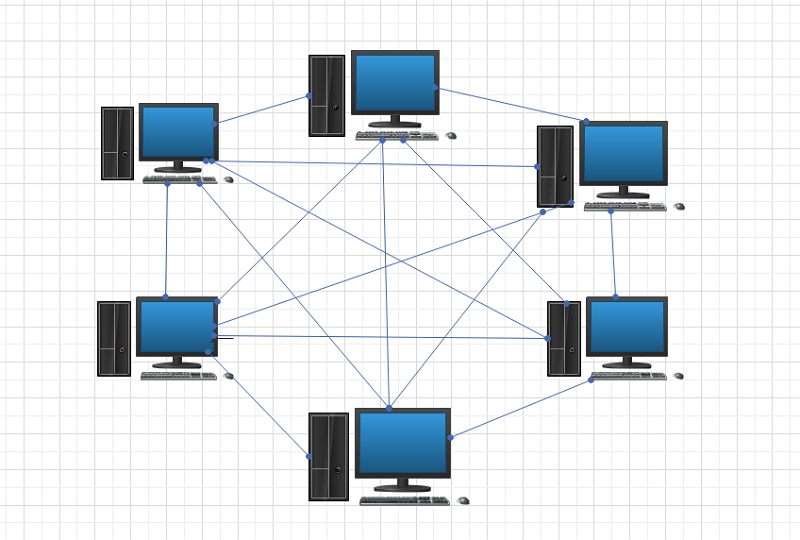
Mesh topology is a type of networking in which all the computers are inter-connected to each other. In Mesh Topology, the connections between devices take place randomly. The connected nodes can be computers, switches, hubs, or any other devices. In this topology setup, even if one of the connections goes down, it allows other nodes to be.
What is mesh topology with example IT Release
mesh network topology (mesh network): A mesh network is a local area network ( LAN ), wireless local area network ( WLAN ) or virtual LAN ( VLAN ) that employs one of two decentralized connection arrangements: full mesh topology or partial mesh topology. In a full mesh topology, each network node (workstation or other device) is connected.

Mesh / Fully connected topology
The Mesh Network Topology Diagram examples was created using ConceptDraw DIAGRAM software with Computer and Networks solution. Mesh Network. Computer and Network Examples. A Mesh Topology is a computer network topology that is based on the cells concept, in which each workstation connects with several other workstations of the same network with.

Mesh Topology Diagram Png Fabric designers have also scaled mesh and ring designs in multiple
Different types of mesh topology. There are two forms of this topology: full mesh and a partially-connected mesh. In a full mesh topology, every computer in the network has a connection to each of the other computers in that network.The number of connections in this network can be calculated using the following formula (n is the number of computers in the network): n(n-1)/2
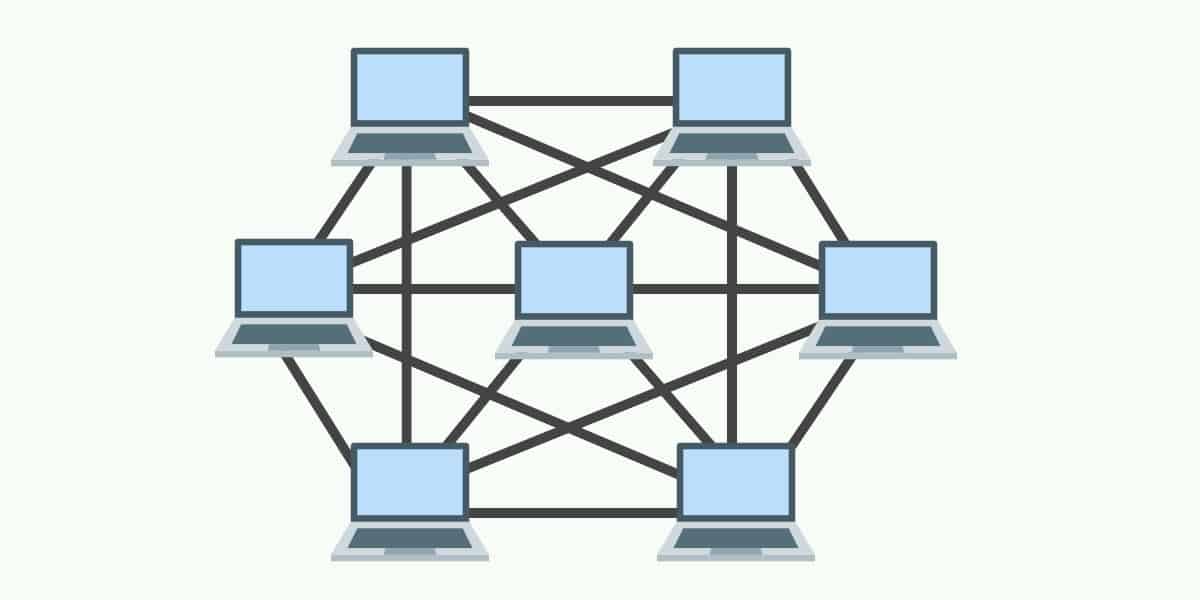
6 Best Network Topologies Explained Pros & Cons [Including Diagrams]
Mesh topology block diagram. Fabric designers have also scaled mesh and ring designs in multiple dimensions, creating fabric configurations called two-dimensional rings or Torus structures. These are very complex topologies that are typically only deployed in applications such as high-performance computing, so we will not go into any detail in.
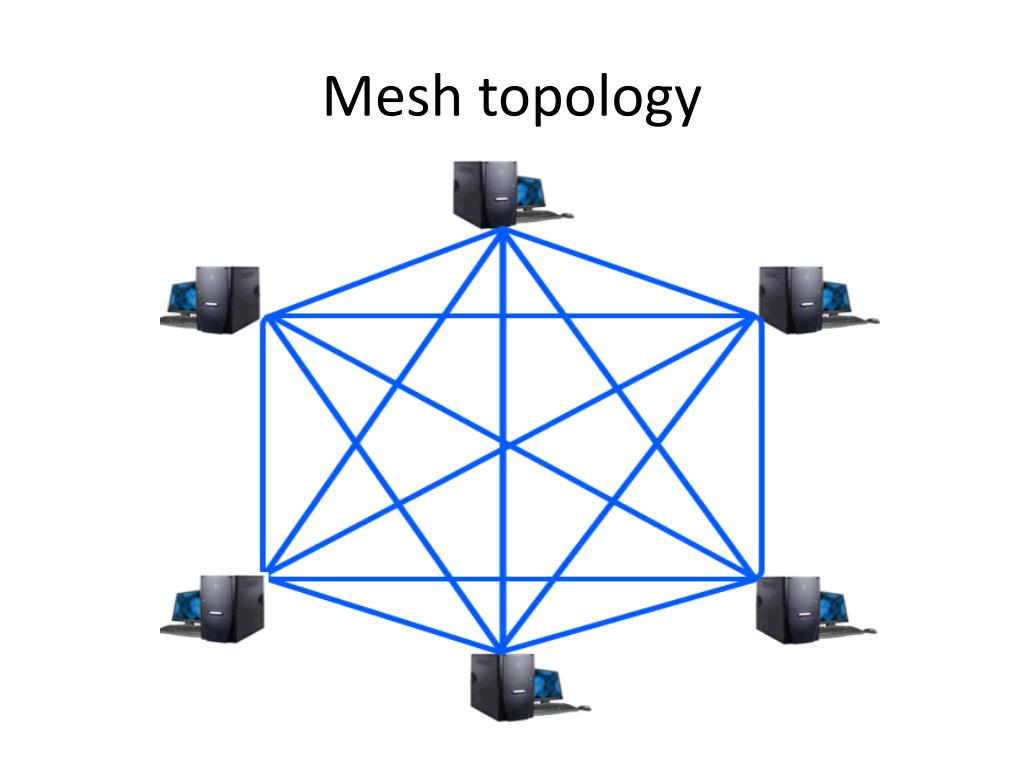
PPT Computer Networks & Topologies PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2488052
Redundancy: Mesh topology diagrams often include redundant connections, which provide backup paths for data transmission. This ensures that if one connection fails, there are alternative paths available for data to reach its destination. Scalability: Mesh topology diagrams can be scaled up to accommodate a large number of nodes and connections.
What are FullMesh, Ring and Hybrid Toplogies, Advantages and Disadvantages of FullMesh, Ring
A mesh network is a local area network topology in which the infrastructure nodes (i.e. bridges, switches, and other infrastructure devices) connect directly, dynamically and non-hierarchically to as many other nodes as possible and cooperate with one another to efficiently route data to and from clients. This lack of dependency on one node.

IMPROVE MY KNOWLEDEGE Mesh topology
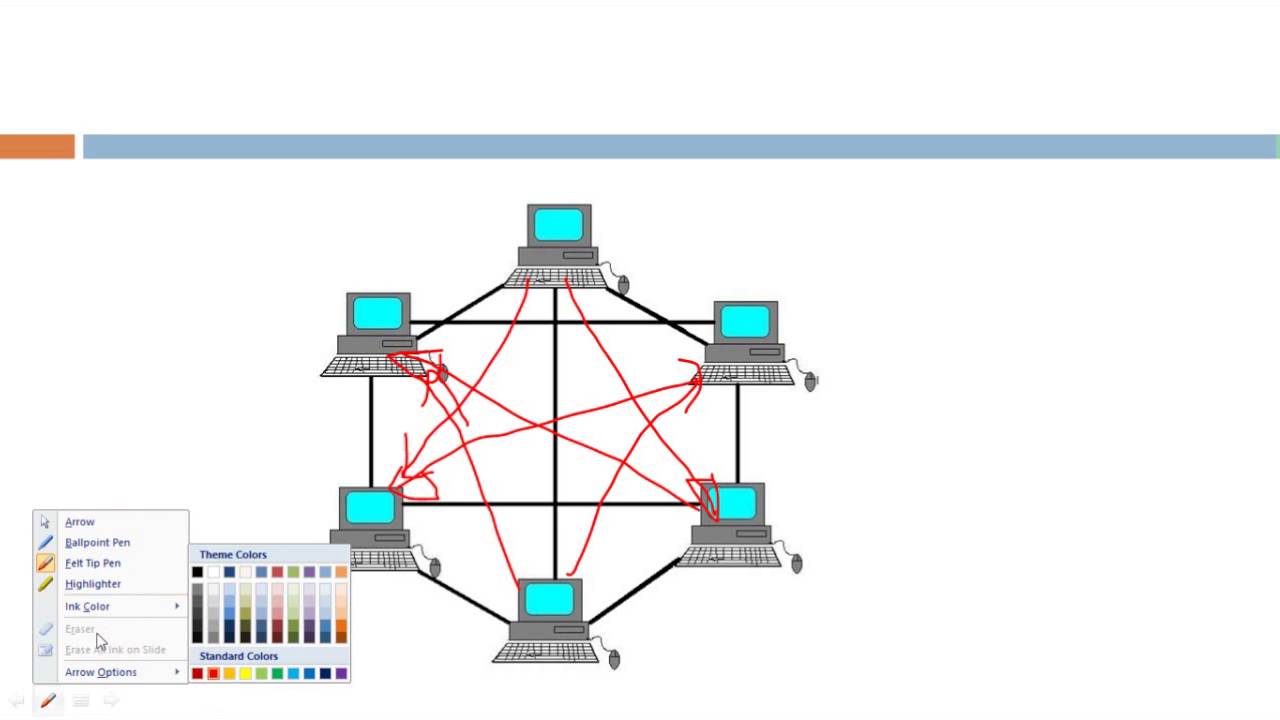
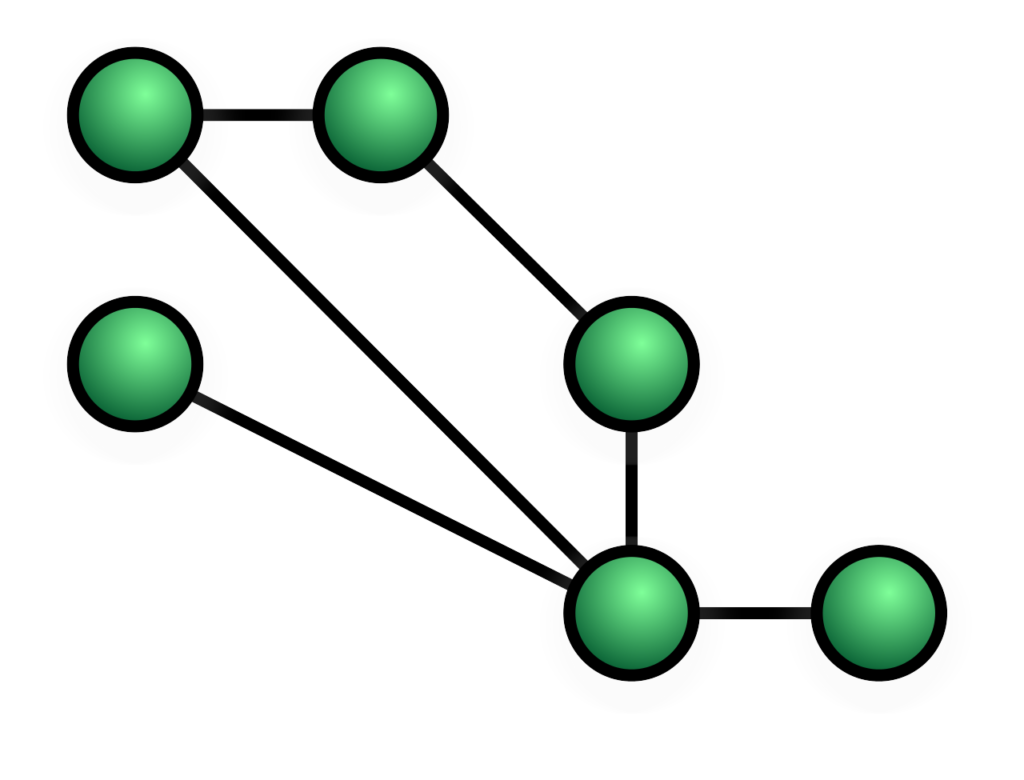
Partial Mesh Topology: In partial mesh topology, each device is connected to only those devices, to which they communicate frequently. This reduces redundant links and saves the setup cost.. For example a combination of star and bus topology is known as star bus hybrid topology, this topology is shown in the above diagram.

An Introduction to Network topology Cablify
Network topology is used to describe the physical and logical structure of a network. It maps the way different nodes on a network--including switches and routers--are placed and interconnected, as well as how data flows. Diagramming the locations of endpoints and service requirements helps determine the best placement for each node to optimize.

Mesh / Fully connected topology
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology : It's costly as compared to the opposite network topologies i.e. star, bus, point to point topology. Installation is extremely difficult in the mesh. Power requirement is higher as all the nodes will need to remain active all the time and share the load. Complex process.
What is mesh topology with example IT Release
Mesh topology is a network setup where several computers and networks are connected. With this topology, you have the power to distribute a large number of transmissions even if one of the network connections fails. Below you can see the mesh topology diagram. Mesh topology was first introduced 30+ years ago for developing military applications.
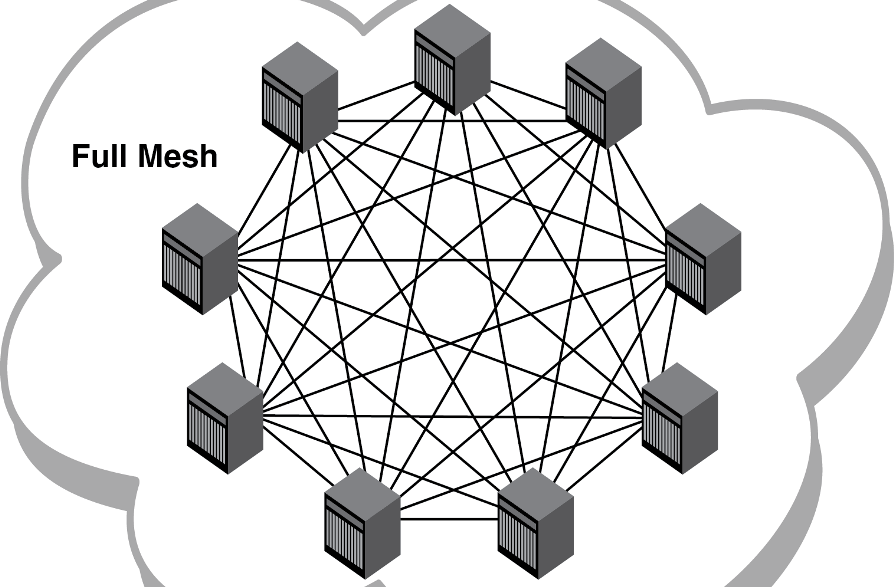
What Is Mesh Topology? Advantages And Disadvantages Of Mesh Topology
Mesh Topology, Types, Diagram, Formula, Advantages/Disadvantages. Definition 1: A mesh topology is a network, where nodes are all connected to each other. The networks can be considered as one type of ad hoc network or example of ad hoc. Mobile ad hoc networks (MANET) and mesh networks are therefore closely related, but MANET also have to deal.
The Logical Network Diagram Explained EdrawMax Online
A mesh network is a complex structure comprising point-to-point connections where the nodes meet. Mesh networks can be either full or partial. In partial mesh, the nodes only have two or three connections, while in an entire mesh topology, all nodes are interconnected. Mesh topologies look like a web; they have two ways to send data: routing.

What is Mesh Topology and Types Propatel
Uses a single cable which connects all the included nodes. Ring. Every device has exactly two neighboring devices for communication purpose. Star. All the computers connect with the help of a hub. Mesh. The mesh topology has a unique network design in which each computer on the network connects to every other.

32+ diagram of mesh network topology RosemaryClare
Mesh Topology. A Mesh Topology network offers a direct connection between any two nodes. Unlike bus or ring topologies, network traffic doesn't have to pass through every node on the network to reach its destination. Nor does network traffic have to pass through a central hub as it does with a star topology.