
Cattle Hoof & Horn
Founded by Greeks from Syracuse in the 7th century BC, Chiaramonte Gulfi would change both its name and location during the course of its history. It was variously called Akrillai by the Greeks, Acrillae by the Romans, Gulfi ("place of pleasure") by the Arabs, and Chiaramonte for several hundred years. Finally, in 1881 it assumed its present name.

SheepHoofAnatomy.jpg (800×562) Hooves, Sheep, Goat feet
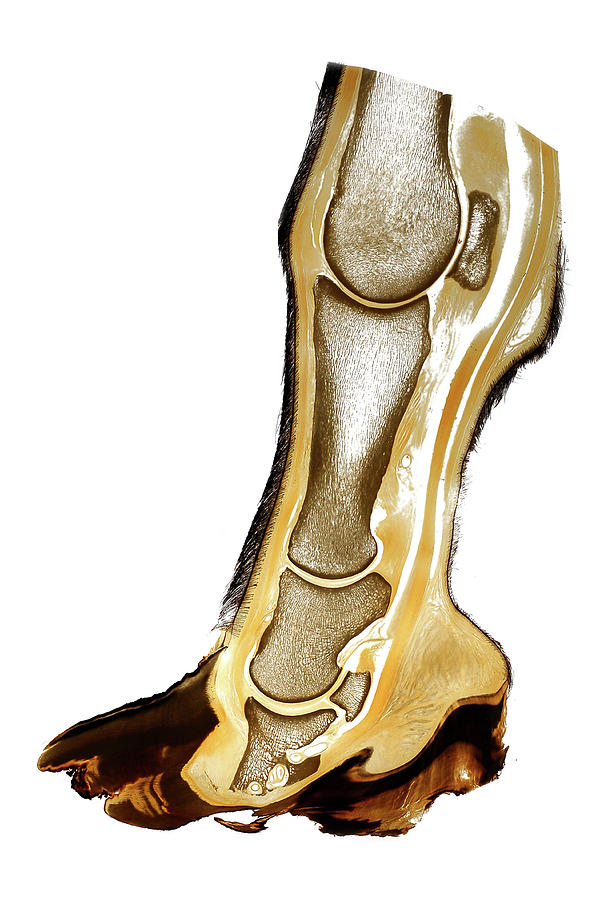
The horse's hoof is a miracle of engineering. It contains a whole host of structures which, when healthy, operate in equilibrium with each other to form a hoof capsule which is able to withstand huge forces, utilising energy to assist with forward movement while providing protection to the sensitive structures beneath.
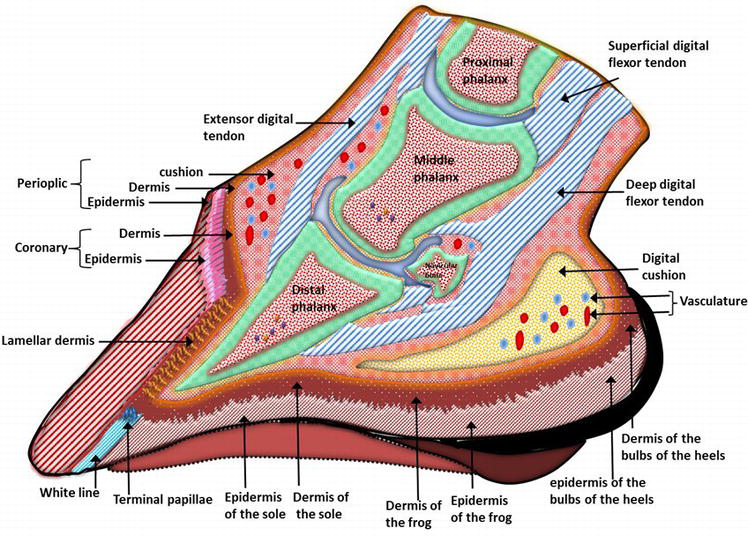
Figure 1.
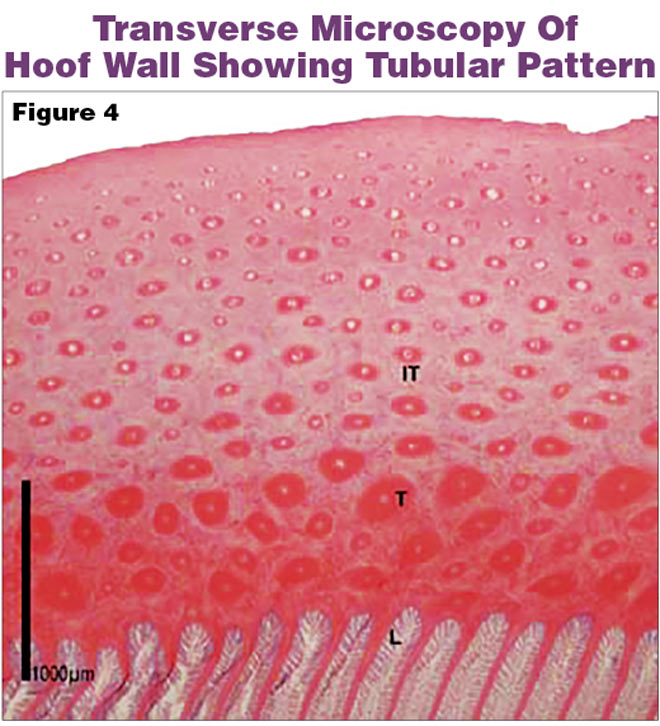
Horn tubules located more peripherally in the hoof wall are smaller (Figure 1) as described by Leach in the mature horse . Table 1 Mean values and (SD) for hoof wall structural variables according to region (dorsal, lateral, medial) of the hooves of 8 foetal Thoroughbreds with ages ranging from 38 days pre-partum to birth.
Outer hoof horn Page 4 Farriers Forum
Horn makes up the outer surface if the hoof and is particularly resistant to mechanical and chemical damage. Each epidermal region of the hoof is associated with a dermal region (corium). The corium are connected to the underlying structures by the subcutis.

The Anatomy of the Hoof Hoofcount
The hoof ( pl.: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. [1] Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits; the ruminants with two digits are the most numerous, e.g. giraffe, deer, bison, cattle, goat, and sheep. [2]

Learning about life and death The Rocky Mountain Collegian
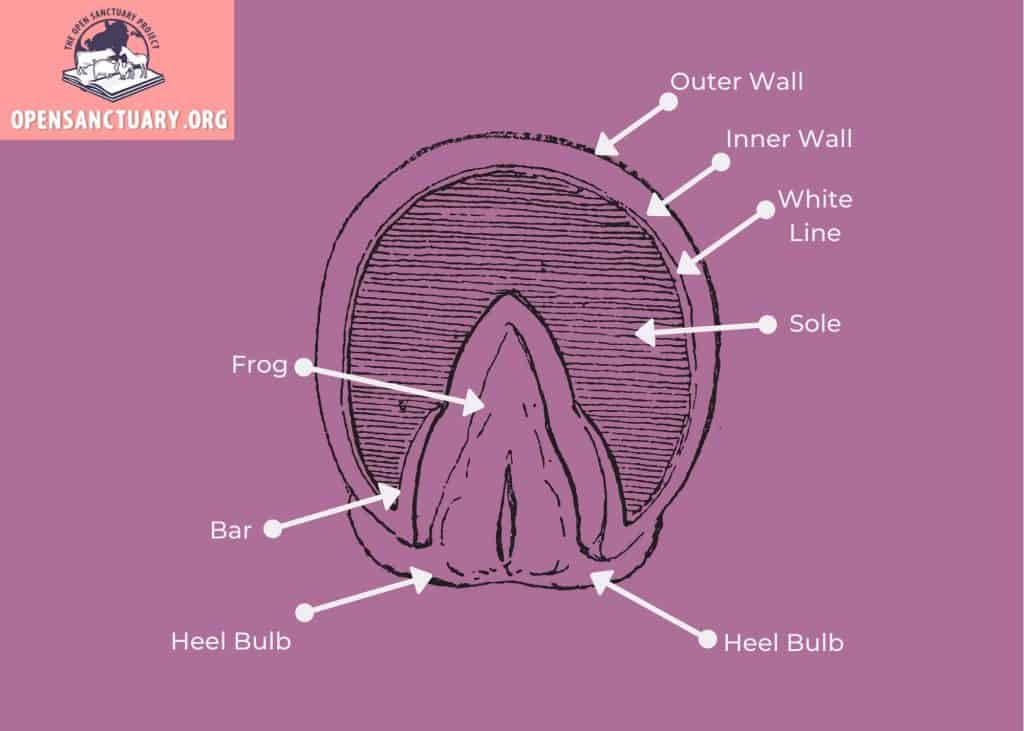
The hoof is an extremely important structure in an animal's body. Hoof wall is equivalent to our fingernails. This is the strongest horn and is crucial for weight bearing. The Frog is equivalent to the foot pad on a dog or a cat. White line is the junction between the wall horn and sole horn. Its made of weaker horn.
What Do Horn Tubules Do? American Farriers Journal
Wall horn: Similar to human fingernails, this part is the strongest and most crucial for weight carrying. Sole horn: Equal to the canine or feline footpad. White line: Comprised of a weaker horn and the intersection between the sole horn and the wall horn. Pedal bone: The major bone of the hoof and similar to that of the end of a human finger.

UniqueHorn Hoof Care producten Dierapotheker.be
The horse hoof is the hard covering of the distal end of each digit. If you are a veterinary student, horse physician, or horse owner, you might know the horse hoof anatomy. It is essential for hoof trimming and shoeing purposes. In this short article, I will discuss the horse hoof anatomy with diagrams and natural pictures.

Antique Swiss STAUBBACH WALKING STICK Mountain Goat Horn Hoof 35" Hardwood Ibex eBay
Healthy hoof horn is resilient and alive, expanding at the heels by much as ¼ inch with each step. The heels dampen energy while the frog and sole support the inner hoof tissues, and the toe propels the horse forward. With each foot impact, the hoof pumps blood circulation through the hoof and up the limb. The collateral cartilages are located.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-157732129-5c32e28a46e0fb0001f87e25.jpg)
Understanding Your Horse's Hooves
Although farriers know that horn tubules play an important role in hoof wall structure, this article provides a deeper understanding of it. The equine hoof wall has a complex tubular structure, which extends across the stratum medium. In a healthy hoof, the tubules are straight, parallel to each other and descend at the same angle as the hoof.

Horn & Hoof Restaurant Docklands, AUVIC OpenTable
Coffin Bone. The coffin (or "pedal") bone is the bottom bone located near the toe and encapsulated in the hoof. It is the largest bone in the hoof and helps to shape the hoof wall. It's surrounded by special tissues that help make-up the laminae of the hoof wall, as well as, the tissues of the sole.

Horn & hoof
The hoof, and its underlying structures, is a type of integument like the skin on the rest of the body. Although there are differences in the way the hoof appears compared to skin, there are many similarities in both structure and response to injury. The skin and the hoof are both composed of three layers: the epithelium, the dermis, and the.
Horse Anatomy The Hoof The Open Sanctuary Project
Hooves help them walk and run on hard ground. In animals such as the horse and antelope, hooves are an adaptation for fast running and lend the animal both speed and endurance. The sharp hooves of some animals are also used for defense. Hooves are made of keratin, or horn, a fibrous protein that is produced by the outer layer of the skin.
Equine laminitis hoof with horn capsule rotation Photograph by Christoph Von Horst Fine Art
The hoof is composed of horn, derived from epidermal tissue which has been keratinised to a varying extent . Horn is largely arranged into a series of parallel microscopic tubules, interconnected by intertubular horn [ 9 ].
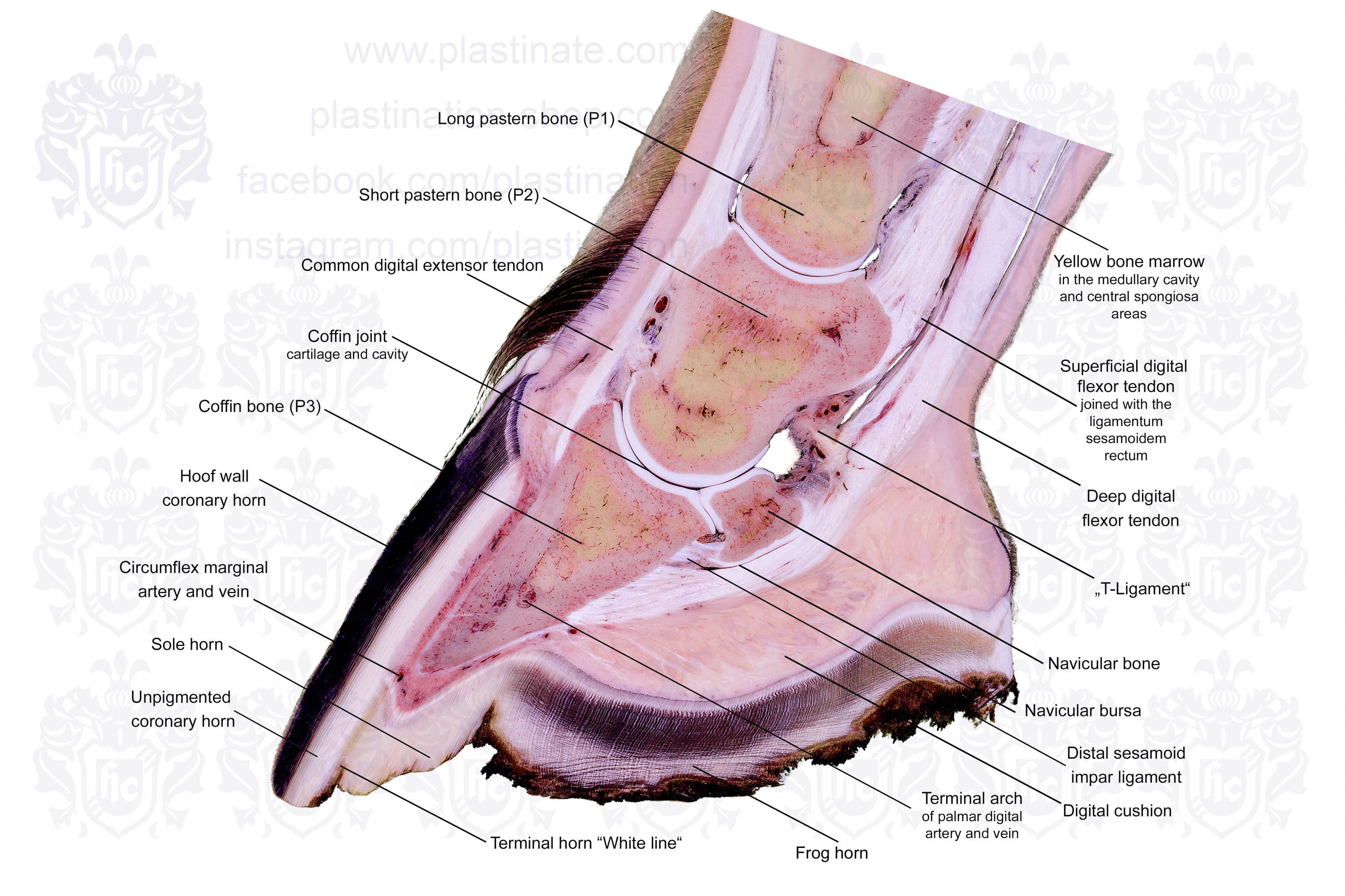
Horse Hoof Anatomy Labelled Teaching Chart Sectional Anatomical Equine Foot Morphology Image
Horn & Hoof Restaurant Docklands is situated in the heart of the Melbourne's food district, only a stone's throw from the Docklands Stadium, This waterfront venue is the perfect location to enjoy a drink with a view, and a truly exceptional European dining experience at the Horn & Hoof Restaurant Docklands.

PEELING LUMPS of HOOF HORN from COWS FEET! YouTube
A corn is a type of bruise that appears in the sole at the buttress (that is, the angle between the wall and the bar). It is most common in the forefeet on the inner buttress. Corns may arise from pressure applied to the sole by the heel of a shoe improperly placed or left on too long.